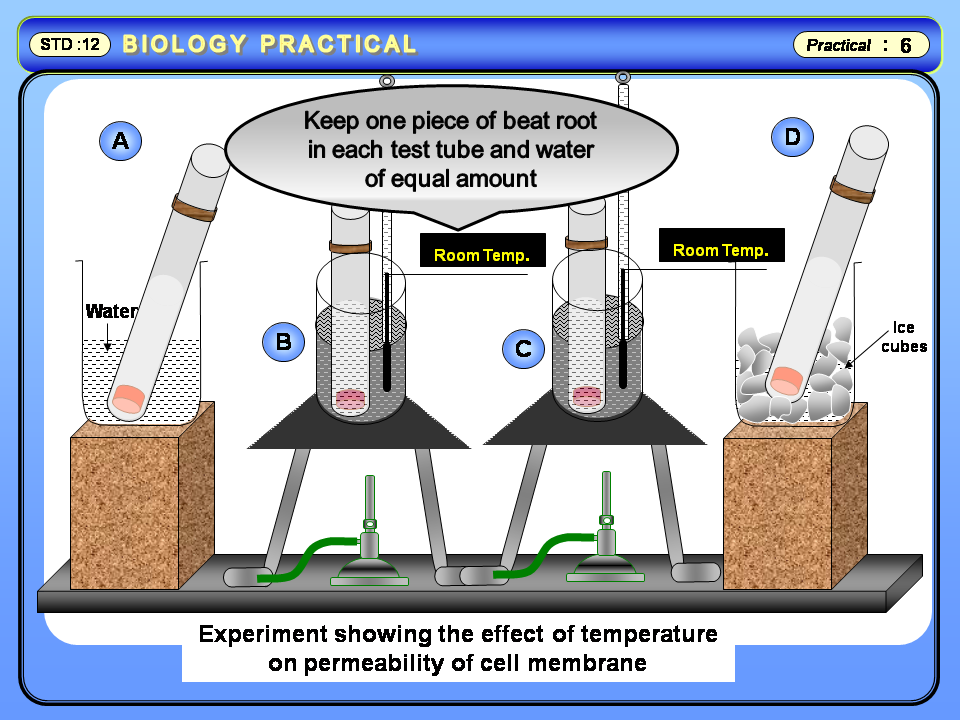
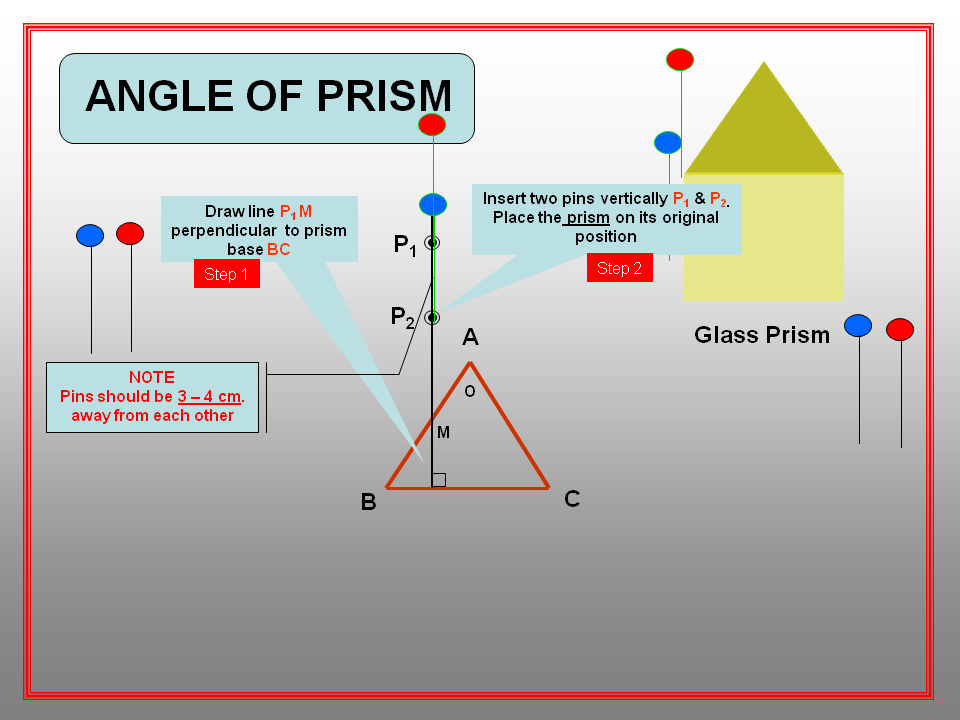
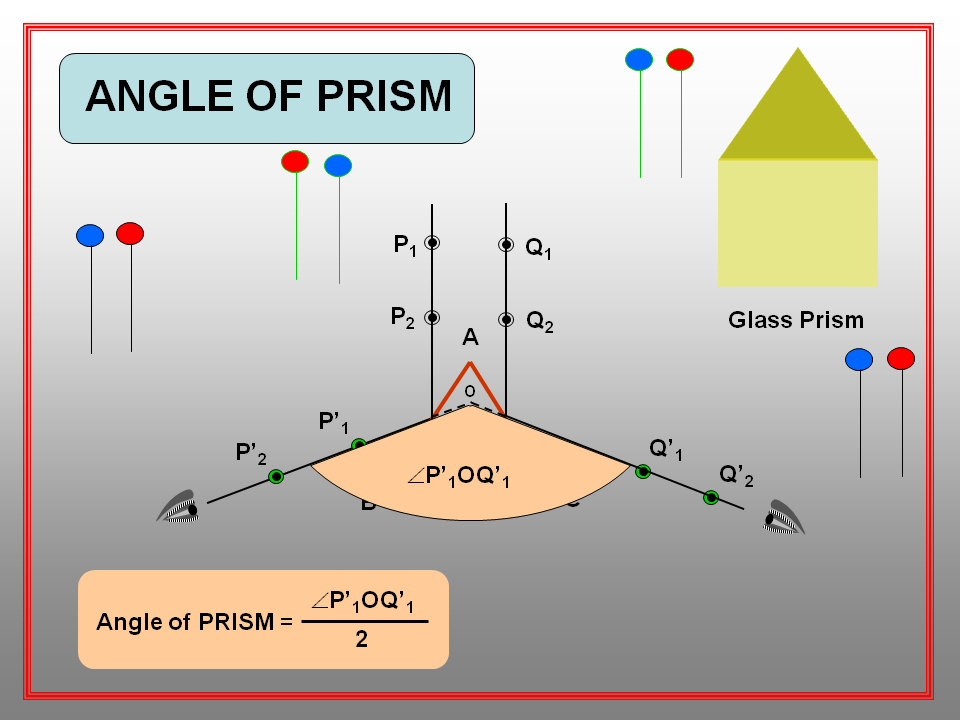
To test the presence of Carbon monoxide and Sulphur dioxide in the atmosphere.
INSTRUMENTS
Filter paper,
Palladium or Platinum chloride, Acidic potasium dichromate.
Test for Carbon monoxide
Filter paper deep in chemical
Keep where transportation is more and smoke of automobiles is very high
View the changes on filter paper.
Slowly slowly it gets change in colour.
After some times
Finally you see the change in colour that is due to Carbon monoxide is presence in Air.
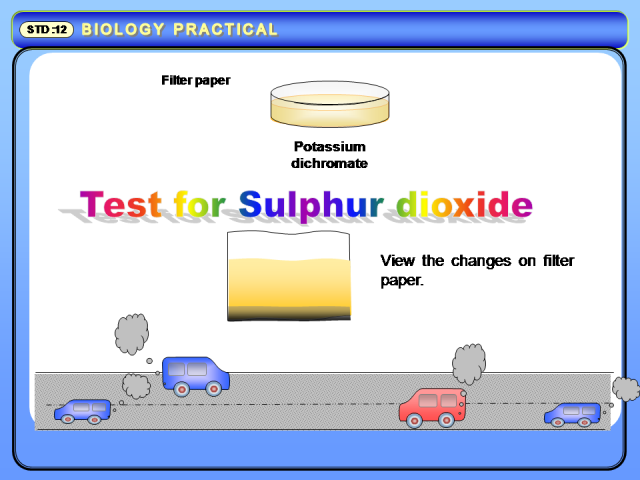
Test for Sulphur dioxide
Filter paper deep in chemical
Keep where transportation is more and smoke of automobiles is very high
View the changes on filter paper.
Slowly slowly it gets change in colour.
After some times
Finally you see the change in colour that is due to Sulphur dioxide is presence in Air.
For more details view Video
 |
| Test of Carbon and Sulphur dioxide |
INSTRUMENTS
Filter paper,
Palladium or Platinum chloride, Acidic potasium dichromate.
Test for Carbon monoxide
Filter paper deep in chemical
Keep where transportation is more and smoke of automobiles is very high
View the changes on filter paper.
Slowly slowly it gets change in colour.
After some times
Finally you see the change in colour that is due to Carbon monoxide is presence in Air.
Filter paper deep in chemical
Keep where transportation is more and smoke of automobiles is very high
View the changes on filter paper.
Slowly slowly it gets change in colour.
After some times
Finally you see the change in colour that is due to Sulphur dioxide is presence in Air.
For more details view Video
To test the presence of Carbon monoxide and Sulphur dioxide in the atmosphere.