Study the Influence of Heat (temperature) and Chemicals on the Release of Pigments from Root and other Tissues of Plant
 |
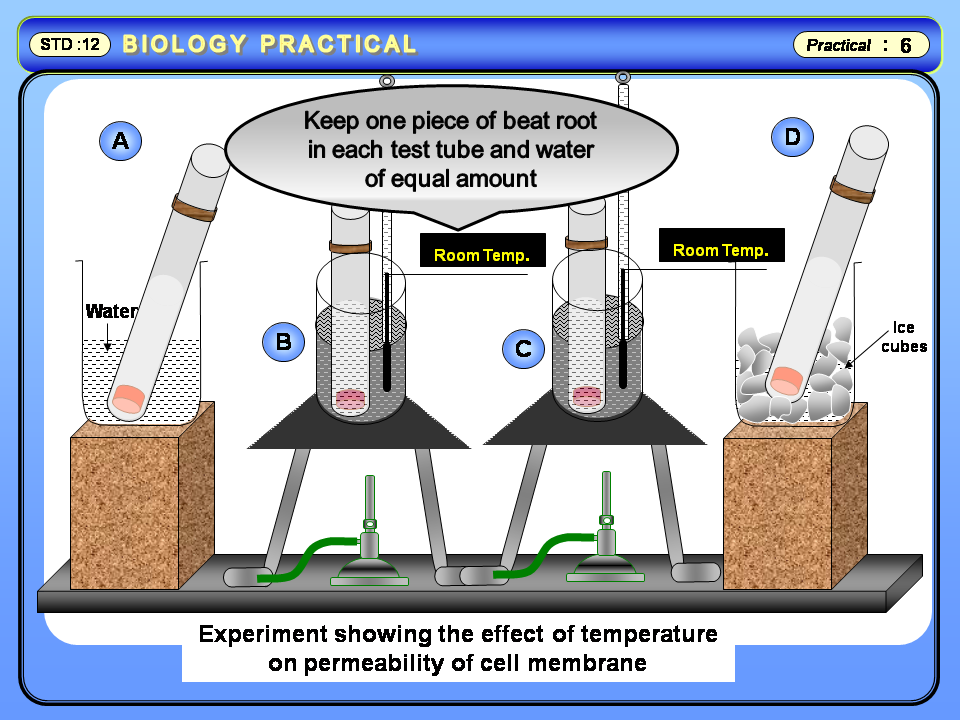
| Influence of heat on Beat root |
AIM :-
To study the influence of heat (temperature) and chemicals on the release of pigments from root and other tissues of plant.
INSTRUMENTS AND MATERIALS
Test tubes, cork borer, blade, beakers, measuring cylinder, thermometer, burner,
Fresh beet roots, alcohol, formalin, benzene, distilled water, ice cubes.
Observation :-
Table 1 : Effect of temperature on leaching of pigments from the beet root.
Conclusion
Betacyabin is present in the cell sap of beet root in vacuoles when beet root is kept at high temperature the permeability of cell membrane is effected. High temperature damages the membrane and pigment leaks out from the membrane. This leaking is maximum at high temperature.
Observation :-
Table 2 : Effect of various chemicals on the permeability on the cell membrane.
Conclusion:
The organic solvents like formalin and alcohol damage the cell membrane by dissolving fat and denaturing proteins. This permeability of cell membrane increases. So more leaking of pigment takes place.
More details view video:
Study the Influence of Heat (temperature) and Chemicals on the Release of Pigments from Root and other Tissues of Plant